In Describing Anxious Attachment Bowlby Used the Example of
Many parents with this type of attachment experience powerful emotional hunger toward their kids as though they are trying to fill the gap left from their childhoods. In anxious-insecure attachment the lack of predictability means that the child eventually becomes needy angry and distrustful.
A Brief Overview Of Adult Attachment Theory And Research R Chris Fraley
John Bowlby came to the conclusion that there is a biological basis for the dynamics of attachment.
. The baby begins to show preferences by for example smiling and vocalizing to and settling more quickly with some caregivers than others. These figures are not treated alike. The different of relationship between children and their caretaker will form the style that they use to interpret the world in the future.
Bowlby 1980 believed that lifes deepest and most intense emotions arise in the foundation of attachment relationships. Referred to as anxious ambivalent attachment in children anxious attachment develops in early childhood. Strong emotional connection that develops between children and primary caregiver Bowlby.
Maternal deprivation internal working model strange situation. It will include supporting research by Shaffer and Emerson Ainsworth and Harlow along with criticisms by Rutter. The underlying assumption of Bowlbys Maternal Deprivation Hypothesis is that continual disruption of the attachment between infant and primary caregiver ie mother could result in long-term cognitive.
Anxious attachment is one of the three insecure attachment styles. The metaphor of attachment which John Bowlby 1969 used to characterize the emotional bond between an infant and his or her primary caregiver implies proximity affection and being fastened on Oxford American Dictionary 1980. Most often anxious attachment is due to misattuned and inconsistent parenting.
There are three kinds of insecure attachment. Attachment Theory Bowlby Summary. Bowlby suggests that this is an evolutionary trait that formed to help children be able to survive.
Crying is the dominant proximity-promoting behaviour though smiling and clingingsnugglingcuddling as also examples that infants and older childrenadults use. John Bowlby psychologist and psychoanalyst proposed the attachment theory throughout the 1950s and 1960s and made notable contributions to the field of psychotherapy for his work on attachment. British psychologist John Bowlby was the first attachment theorist describing attachment as a lasting psychological connectedness between human beings Bowlby was interested in understanding the separation anxiety and distress that children experience when separated from their primary caregivers.
Attachment Theory describes Bowlbys 4 stages of attachment of the close relationships we form in early childhood and adulthood. According to Bowlby almost from the beginning many children have more than one figure toward whom they direct attachment behaviour. Bowlby 1982 developed attachment theory in order to describe the different ways both secure and insecure that children attach to parents or caregivers.
Bowlby believed the attachment. Low self-esteem strong fear of rejection or abandonment and. Attachment style is a theory base from John Bowlby Psychologists attachment theory.
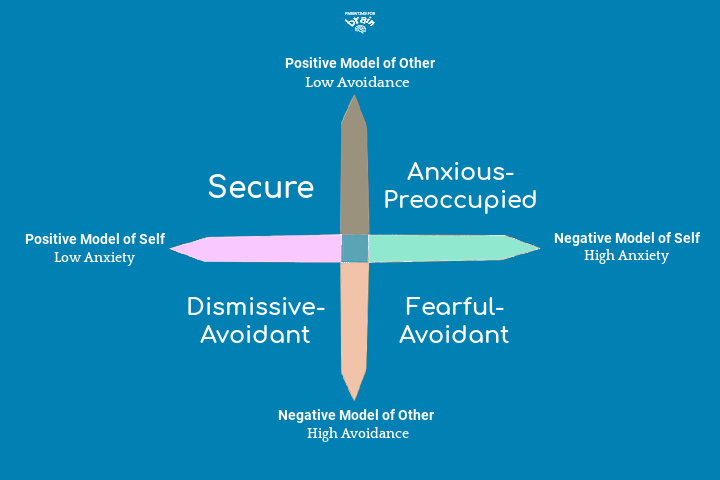
The concept of attachment styles grew out the attachment theory and research that emerged throughout the 1960s and 1970s. Amir Levine author of Attached says that 50 of people have a secure attachment 25 an avoidant attachment 20 anxious attachment and the rest falls into the fearful category with unhealthy traits from both. Bowlby is describing here is attachment behaviour.
During early childhood these attachment styles are centered on how children and parents interact. During this formative period a childs caregiver may have acted nurturing and responsive one minute and unavailable or insensitive the next. Proximity Seeking In phase 3 of attachment formation 6 months infants shift from exclusively using proximity-promoting behaviours to using proximity-seeking or go there.
Avoidant anxious and disorganized Cassidy 2008. He feels scared calls for his mother - hearing her voice he runs to her. Attachment Theory is a psychological model describing the stages of attachment of the close relationships we form in early childhood and as adults.
John Bowlby 1907-1990 British child psychiatrist and psychoanalyst known for his theory on attachment. Bowlby used the term monotropy to describe this bias. Although Bowlby did not dispute the possibility of children forming multiple bonds with different people he still upholds the view that since it is the first.
Attachment theory emphasizes the importance of a secure and trusting mother-infant bond on development and well-being. Bowlby used the term maternal deprivation to refer to the separation or loss of the mother as well as failure to develop an attachment. For example - Tom who is 2 years old hears an unexpectedly loud noise.
They start to develop stranger anxiety An unknown face is neither pleasurable nor exciting to the baby. It is a theory that is based on the idea of imprinting that can be found in most animal species. Known as anxious preoccupied attachment in adulthood anxious ambivalent attachment typically develops in children in the first 18 months of life.
Instead it signals danger. Attachment theory was first suggested by John Bowlby after World War II and since then has been the subject of literally thousands of research studies. Answer 1 of 5.
Bowlby noticed that if children are separated from their parents at an early age their future romantic relationships were more likely to suffer. In adulthood attachment styles are used to describe patterns of attachment in romantic relationships. Sudden biologically primed form of attachment demeonstrates the critical period.
For example the child may. There is a strong bias for a child to direct attachment behaviour mainly toward one particular person. The essay will describe the two theories weighing up the strengths and the weaknesses.
There is research that shows that children of parents who exhibit an anxiousambivalent attachment style will inevitably use that same style when raising their children. In John Bowlbys Attachment Theory the suggestion is that a child is born with programming that helps them to form an attachment to others. This essay will describe and evaluate Bowlbys theory of attachment and maternal deprivation hypothesis.
How Anxious Attachment Can Make You Feel Jealous. Free attachment style quiz. He developed the notion of internal working model to describe how the infant sense of self became codified through interactions with the mother or caregiver.
If their relationship is good children will think tha. If you are not yet sure which attachment style you are take a free test here. Conflicted responses very upset but difficullt being comforted.
On reaching her he relaxes and leaves her side to carry on playing. A secure attachment is what makes for a healthy parent-child relationship. Bowlbys concept of internal working models was a catalyst for the increased interest in the continuity of attachment patterns from infancy through adulthood Westen et al 2006.
A Brief Overview Of Adult Attachment Theory And Research R Chris Fraley

Attachment Theory A Social Neuroscientist S Perspective Dr Pascal Vrticka Phd Fhea
No comments for "In Describing Anxious Attachment Bowlby Used the Example of"
Post a Comment